
Project Introduction
Tensile strength test can also be called tensile test for metal mechanical properties. Tensile test can measure a series of strength indexes and plastic indexes of materials. Strength usually refers to the ability of a material to resist elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and fracture under external force. Plasticity refers to the ability of a metal material to deform plastically under load without damage. Commonly used plasticity indicators are elongation and shrinkage.
Guideline
Reference standard for tensile strength test
GB-T228-2002 Metallic materials Tensile test method at room temperature
ASTM E8-04 Metal Tensile Test Method Metal Tensile Strength Test
EN 10002-1:2001 Tensile test of metallic materials, normal temperature test method
JIS Z 2241:1998 Metallic material tensile test method
ISO 6892:1998 Metallic materials, tensile test at ambient temperature
experiment procedure
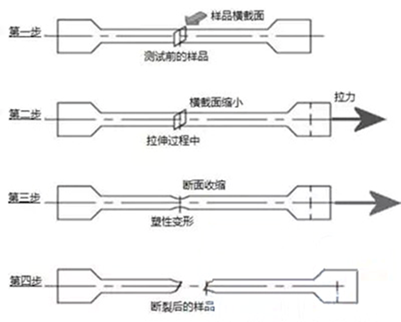
Elastic zone (from 0 to yield strength YS)
· Less elongation: corresponding percentage.
· Elastic elongation: If the stress stops, the sample will return to its original length.
· Yield strength: when the permanent elongation value reaches 0.2%.
· Yield strength = force at yield (N) / original area of the tensile specimen (mm2) or the same MPA value.
· Longitudinal modulus: ratio of applied force to elongation length (depending on metal).
· Transverse modulus: the ratio of elongation to interface shrinkage (applies to all metals ~ 0.3).
Plastic zone (from tensile strength UTS to yield strength YS)
· Large elongation: a few percent for general metals, up to 50 to 60 percent.
· Inelastic elongation: if the stress stops, the specimen remains permanently strained.
· Breaking force: record of tensile strength (UTS).
· Tensile strength = maximum force (N) before breaking the tensile test / original area of the tensile specimen (mm2) or the same MPA value.
· Due to the cold work effect, the strain will continue to increase with the test.
After breaking
· The overall length needs to be measured to calculate the elongation.
· E% = (Lu – L0) / L0 x 100 (Lu is the final length, L0 is the initial length).
Young's modulus-important parameter
· Modulus of elasticity E: unit N/mm2.
· Yield strength YS 0.2: Unit N/mm2 or MPa.
· Transverse modulus: Poisson coefficient, always around 0.3.
· Breaking force: UTS, unit N/mm2 or MPa, except in special cases.
· Elongation at break E%: ductility, E<5% is brittle (brittleness).
· Executive standards: NF EN 10002 and ASTM E8, the difference between the two is the measurement difference (L0) of different elongation values.

Label printers entering the Brazilian market, ANATEL certification is an essential passport! It is the recognition of the Brazilian Telecommunications Authority for the safety and compliance of electronic products, without which products cannot be legally sold.

SRRC certification is not only a guarantee of product compliance, but also a key to opening up the market.

FCC ID certification is a mandatory certification for electronic products by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States, and it is essential for label printers to obtain this certification.
Tensile strength test can also be called tensile test for metal mechanical properties. Tensile test can measure a series of strength indexes and plastic indexes of materials. Strength usually refers to the ability of a material to resist elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and fracture under external force.
Get a quote